Question 1:
Answer the following questions.
(a) What is a 'cell' ?
(b) Name the different organelles in a cell ?
(c) What are micro-organisms ?
(d) which are the different types of micro-organisms ?
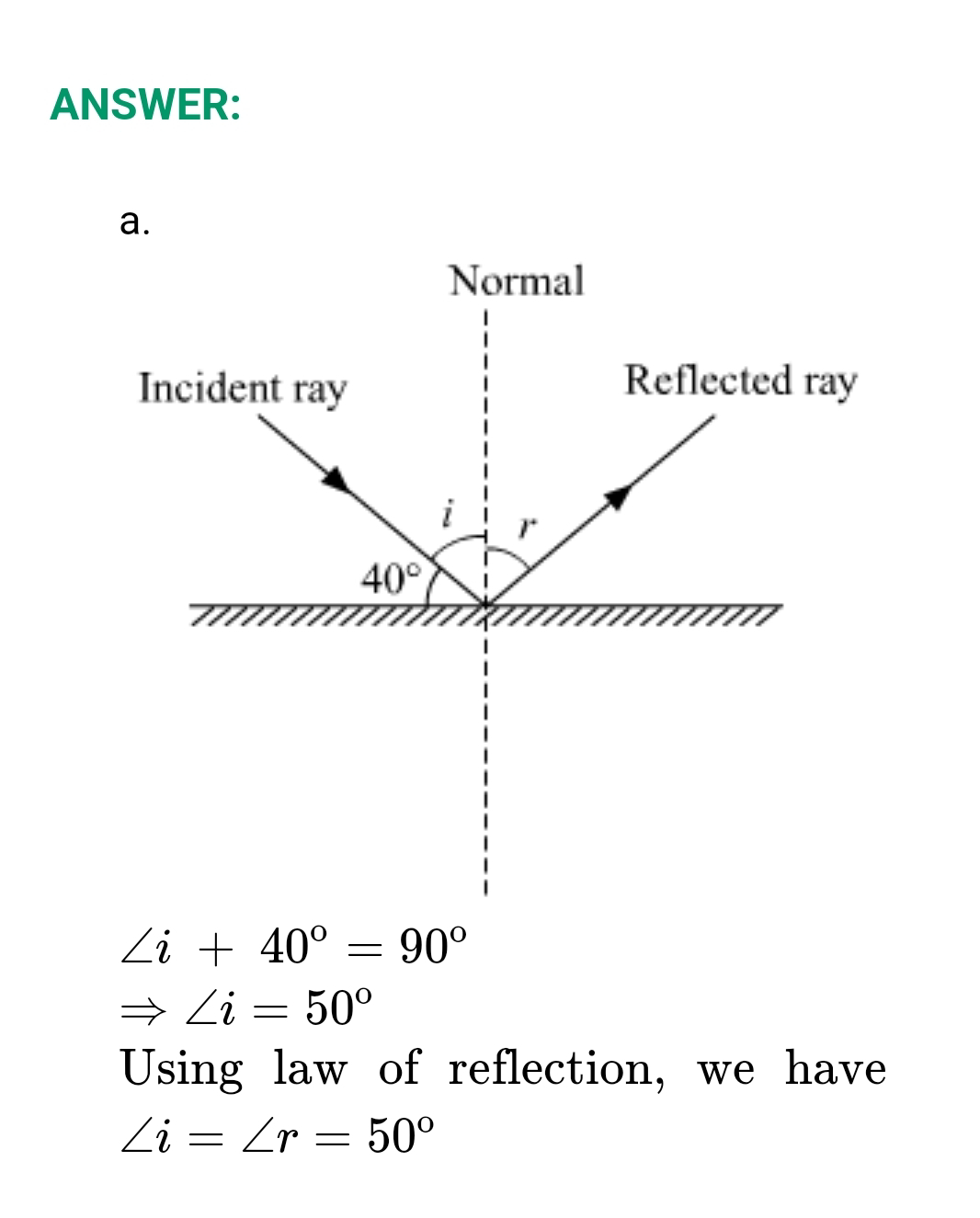
ANSWER:
a. Cell is the smallest unit of life. They are the structural, functional and biological uits of life. The discovery of cells was first made by Robert Hooke. While examining a section of a cork under the microscope, he observed small compartment-like structures and named them cells. However, Hooke observed dead cells under the microscope as cork is made up of dead cells. Cells exhibit different types of properties like:
- It is the smallest living unit of life.
It is so small that it is not visible to the naked eye.
The shape of the cell varies in different organisms and within an organism.
Size of cells also differs.
All living cells exhibit certain basic characteristics like respiration, growth, metabolism, etc.
- Cells originate from a pre-existing cell. A mother cell divides to produce daughter cells. Hence, cells exhibit cell division.
b. The cells may conatin the following cell organelles depending upon wether it is a plant or animal cell:
Cell membrane, cell wall, vacuole, plastids, endoplasmic reticulum, chloroplast, golgi apparatus, ribosomes, mitochondria, nucleus, lysosomes, centrosome and inclusion bodies.
c. Living organisms which are not visible to the naked eye are known as micro-organisms. They are living organisms that can be seen only with a microscope or a magnifying glass. Microorganisms were observed for the first time by Anton von Leeuwenhoek in 1674, using a microscope of his own.
d. Microorganisms can be divided into 5 major groups like:
Bacteria- Bacteria are the most primitive and diverse unicellular organisms found in living world. They are prokaryotic in nature as their genetic material, i.e. DNA, is not enclosed within a nuclear membrane. Because of their unique biochemical pathways and properties, they are of high economic importance to the human beings.
Fungi- Fungi is a group of eukaryotic, unicellular as well as multicellular, non-photosynthetic organisms that includes mushrooms, moulds and yeasts. These organisms have a rigid cell wall made up of chitin and are found in diverse shapes and sizes.
Algae- Algae are a diverse group of aquatic organisms that have the ability to conduct photosynthesis.
Protozoa- Protozoa are a group of unicellular micoorganism which are non photosynthetic in nature. Many protozoa cause disease in animals and humans.
Viruses- Viruses are ultra microscopic and non cellular organisms. They have simple structure having genetic material coated by protein coat. They are obligate parasites and highly pathogenic.
Page No 80:
Question 2:
Fill in the blanks with the proper word.
(a) The organelle called the ........... is present in plant cells only.
(b) Garbage is converted into .......... by micro-organisms.
(c) In the cell, photosynthesis is carried out with the help of ............ .
(d) An electron microscope is necessary for the study of ............ .
ANSWER:
(a) The organelle called the chloroplast is present in plant cells only.
(b) Garbage is converted into compost by micro-organisms.
(c) In the cell, photosynthesis is carried out with the help of chloroplast.
(d) An electron microscope is necessary for the study of cells .
Page No 80:
Question 3:
What is difference between us ?
(a) Plant cell and animal cell.
(b) Prokaryotic cell and eukaryotic cell.
ANSWER:
a.
| | Animal cell | | Plant cell |
i. | Animal cells are smaller in size. | i. | Plant cells are comparatively larger. |
ii. | They lack a cell wall. | ii. | Cell wall is the outermost structure in a plant cell. |
iii. | They lack plastids except Euglena. | iii. | Plastids are present in all plant cells. |
iv. | Many vacuoles are present and they are smaller in size. | iv. | They have a single large central vacuole. |
v. | They have centrioles. | v. | They lack centrioles. |
b.
Characteristics
| Prokaryotes | Eukaryotes |
| Size of the cell | Cells are small in size. |
Cells vary in size and are generally larger than those in prokaryotes.
|
| Nucleus | No nucleus with a nuclear membrane is present. |
There is a well-defined nucleus with a nuclear membrane.
|
| Membrane-enclosed organelles | Organelles having a membrane around them (e.g., mitochondria, plastids) are absent. |
Membrane-enclosed organelles are present.
|
| Cell wall | Cell wall is usually present. It is composed of peptidoglycan. |
Cell wall is usually present in plant cells. It is composed of cellulose.
|
| Genetic material |
The genetic material is present as nucleoid, i.e., a properly defined nucleus is absent.
| The genetic material is present inside the well-defined nucleus.
|
Page No 80:
Question 4:
Sketch and describe in your own words, the plant cell and animal cell.
ANSWER:
Diagram
Plant cell
Cell membrane: A cell is composed of cell membrane, cytoplasm and nucleus. The cytoplasm and nucleus enclosed in the cell membrane together constitute the plasma membrane. It checks the transport of substances in the cell.
Cell wall: In plants, an extra protective covering known as cellulose is present. It is called cell wall and protects the plant cell from environment variations.
Cytoplasm: It is a jelly-like substance present between the cell membrane and nucleus. It contains various cell organelles such as mitochondria and Golgi body.
Nucleus: It is a dense spherical body located at the centre of the cell. It is surrounded by a porous nuclear membrane. It contains a spherical body called nucleolus and thread-like structures called chromosomes. Chromosomes are the structures that carry genes and play an important role in inheritance. The entire living substance in a cell is known as protoplast.
Vacuoles: Vacuoles are fluid-filled membrane-bound structures in the cell. In plant cells, a single large vacuole is present. In animal cells, numerous small vacuoles are present.
Plastids: They are present only in plant cells. Chloroplast is a plastid containing the green pigment called chlorophyll, which is required for photosynthesis.
Mitochondria: They are involved in cellular respiration, and hence, are called ‘power houses of the cell’.
Animal cell
Diagram
All the cell organelles in plant and animal cells are same except that animal cells have plasma membrane in place of cell wall and it does not contain chloroplasts.
Page No 80:
Question 5:
Explain the uses and the harmful effects of micro-organisms.
ANSWER:
Microorganisms have found widescale application in various industries. Some of their applications are:
Use of Microorganisms in Food Industry
(i) Lactobacillus bacterium promotes the conversion of milk into curd.
(ii) Yeast is used in preparation of breads, pastries, and cakes.
Use of Microorganisms in Vaccine Production
(i) Protection of the body from the attack of various disease-causing microorganisms through vaccines is known as vaccination.
(ii) Vaccine includes dead or weakened microbes that trigger the production of antibodies in the body.
Use of Microorganisms in Increasing Soil Fertility
(i) Blue green algae and Rhizobium are called biological nitrogen fixers.
(ii) They fix atmospheric free nitrogen to enhance soil fertility.
These are just few examples which highlight the commercial importance of these microorganisms. However, they are not always beneficial can lead to various kinds of damage. This damage can be in terms of health of humans and animals, crop production etc. There are various kinds of microorganisms which are known to cause disease in humans and animals.
Human disease | Pathogen |
Tuberculosis Measles Chicken pox Polio | Bacteria Virus Virus Virus |
Cholera Typhoid | Bacteria Bacteria |
Similarly there are certain species of microorganisms which cause disease in plants and affect the crop productivity.
Plant disease | Pathogen |
Citrus canker | Bacteria |
Rust of wheat | Fungi |
Yellow vein mosaic of bhindi (okra) | Virus |
Page No 80:
Question 6:
Give reasons.
(a) Diseases spread on a large scale during periods of heavy rainfall and floods.
(b) There is a possibility of food poisoning if we eat stale food.
(c) Soil is turned over during tilling.
(d) Fungus grows quickly in moist or humid conditions.
(e) A refrigerator is used in almost every home.
(f) Bread 'rises' during baking.
(g) Fodder is soaked in water before offering to cattle.
ANSWER:
a. Diseases spread on a large scale during periods of heavy rainfall and floods because it provides the optimum conditions for the growth of vectors which transmit diseases. After heavy rainfall and floods, water gets accumulated at places and acts as breeding grounds for mosquitoes and other vectors. These vectors lead to transmission of the microorganisms to their host and result in the development of disease.
For example, malaria is caused by a virus which is transmitted by a mosquito.
b. There is a possibility of food poisoning if we eat stale food because there are chances that it can be infested by microorganisms. Bacteria and fungi can infect the foods which are stored for longer durations of time. For example, the greenish powdery substance which is seen on stale breads is an example of fungus infection.
c. Tilling is a mechanical procedure of agitating soil where the top layer is mixed with the lower layers of soil. This promotes the mixing of organic matter throughout the soil and also promotes the growth of microorganism. These microorganisms help in the conversion of organic matter.
d. Fungus grows quickly in moist or humid conditions because these are the favourable conditions for its growth. Fungus is not seen growing in areas which are well exposed to sunlight.
e. Refrigerator is used in almost every home because it prevents the spoilage of food. Refrigerator provides an optimum environment for storage of vegetable, fruits, cooked and uncooked food. If an optimum temperature is not provided, it can lead to the growth of bacteria and fungi thus leading to spoilage of food.
f. Bread rises during baking because of addition of yeast to its dough. Yeast cells respire anaerobically and liberates CO2 in the process. When yeast cells are added to the bread dough, they utilise the nutrients (carbohydrates) found in the dough and respire anaerobically. Also, they multiply at a very fast rate under such favourable conditions. As a result of the growing bacterial population, large amount of CO2 is released that makes the dough very soft and fluffy, and thus improves the quality of the bread.
g. Fodder is soaked in water before offering it to cattles because it may contain seeds which have been left behind after harvesting. Soaking this fodder helps in the sprouting of these seeds/grains and thus increases the nutritional value of the fodder.
Page No 80:
Question 7:
When will you use a simple microscope and when, a compound microscope? Explain in detail how you will use them.
ANSWER:
The simple microscope is generally considered to be the first microscope which was created by Antony van Leeuwenhoek in the 17th century. It was essentially a type of which was used by Leeuwenhoek to gain information about biological specimens, including the difference in shapes between red blood cells. Today, simple microscopes are not used often because the introduction of compound microscopes which have better resolution and magnifying power.
Compound microscope offers better magnification than a simple microscope. These devices provide a magnification of 1,000 times. It can be used to observe micoorganisms like bacteria, fungi, protozoa etc. It can be used in their detailed study, for example studying their structures.
.png)




.png)






